Why Do Stem Cells Have a Significant Role in Regenerative Medicine?
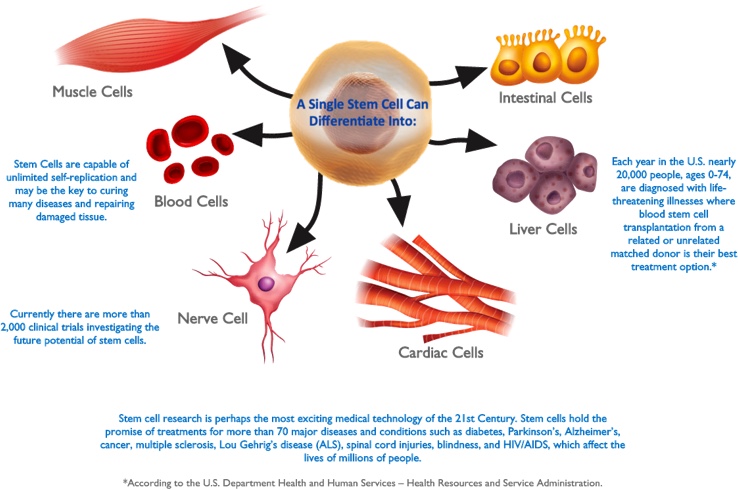
Stem cells display the unique ability to self-renew (to divide and give rise to other stem cells) and to differentiate along specific molecular pathways to form specialized cells. The promise of regenerative medicine is to restore body functions and to cure previously untreatable diseases and injuries.
The study of regenerative medicine includes a variety of different types of stem cells, e.g. adult, mesenchymal, induced pluripotent and embryonic stem cells, each of which holds a unique property in the regeneration process of the human body. Many regenerative therapies discussed in the lectures within ASTEP utilize the patient’s own stem cells. For example, a patient’s own stem cells can be activated through a process of mobilization, where a growth factor protein releases the stem cells from the bone marrow into the peripheral blood. These stem cells now circulate through the blood to naturally repair organs and tissues.
The use of stem cells in regenerative medicine has been a popular topic in the mainstream media as well as the scientific community. On a daily basis discoveries and novel treatments are being developed to treat and manage patients with chronic diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, heart disease, cancer, diabetes and neuromuscular disorders. Stem cell based therapies give physicians the opportunity to treat patients suffering from a wide range of disorders which current treatments are not able to help, making this the field of medicine that can change the paradigm of our current healthcare system.
